First published in Accountancy SA
In South Africa, everyone is talking about the Fourth Industrial Revolution or 4IR, but when leaders including politicians are asked “What is the 4th Industrial Revolution?” and when they can’t answer, the proverbial question that follows is, “So what is the 3rd Industrial Revolution then?”
Could the reason that South Africans are slow or scared to embark on this journey is because they don’t know what it is? All they know is that it will cause them to lose their jobs (so they have heard).
Let’s explore the various industrial revolutions and their impact on jobs.
The First Industrial Revolution took place from the 18th to 19th centuries in Europe and North America. It was a period when mostly agrarian, rural societies became industrial and urban. The iron and textile industries, along with the development of the water wheel and then the steam engine, played central roles in the Industrial Revolution.
The impact of the First Industrial Revolution was felt on the agricultural community. Work was predominately performed by hand. People who no longer were able to farm as their land got taken over by factories, reskilled to become boiler makers, ironsmiths, mechanics, etc as these industries now has machines that need to be fabricated or repaired. These skills were previously in low demand. There was short-term job losses, but different jobs were created that did not previously exist.
The Second Industrial Revolution took place between 1870 and 1914, just before World War I. It was a period of growth for pre-existing industries and expansion of new ones, such as steel, oil and electricity, and used electric power to create mass production. Major technological advances during this period included the telephone, light bulb, phonograph and the internal combustion engine. With the transition from steam power to electricity, there may have been short-term job losses but if the steam mechanics reskilled to electricians, they would have retained their jobs. Yet again there were new skills to be acquired that previously did not exist. Also, with mass production lines, more jobs were created than previously required.
The Third Industrial Revolution, or the Digital Revolution, refers to the advancement of technology from analogue electronic and mechanical devices to the digital technology available today. The era started during the 1980s. Advances during the Third Industrial Revolution include the personal computer, the Internet, and information and communications technology (ICT). Mass production with small batches but with wider varieties was possible. Jobs got replaced by computers and robots, however if you weren’t computer literate then you may have who lost their jobs. Yet again, new jobs were created that previously did not exist e.g. software and hardware engineers and a whole logistics industry was expanded to cater for increased, centralised production volume and a need to distribute to connsumers.
The Fourth Industrial Revolution builds on the Digital Revolution, representing new ways in which technology becomes embedded within societies and even the human body. The Fourth Industrial Revolution is marked by emerging technology breakthroughs in a number of fields, including robotics, artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, quantum computing, biotechnology, The Internet of Things (IoT), decentralized consensus, 3D printing and autonomous vehicles. The biggest impact of the Fourth Industrial Revolution is to improve the quality of life, reduce inequality of the world’s population and raise income level.[1]
The previous industrial revolutions predicted mass job losses, but history can tell us that this was not true. In fact, jobs were created and living standards improved.[2] For this, the 4th Industrial Revolution, the fear is that unskilled workers will be replaced by machines but also workers in skilled professions like medicine and finance too will be replaced. The key strategy for this and previous industrial revolutions is to retrain and reskill and transform the workforce. History has proven that more jobs are created in new field and areas. Humans and machines need to work together, and the role of a data scientist previously not required comes to fore.
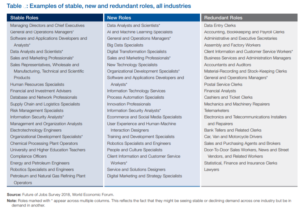
Instead of wasting time worry about your job, rather spend the time reskilling yourself to be ready for your new role. All you need to do is to choose one. The table[3] below could guide you to a new or revised role.
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fourth_Industrial_Revolution
[2] https://bigthink.com/technology-innovation/fourth-industrial-revolution
[3] http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Future_of_Jobs_2018.pdf
In summary, each industrial revolution has brought the fear of job losses, history has proven that this is untrue. The question is “Are you ready to reskill to take advantage of the Fourth Industrial Revolution?”